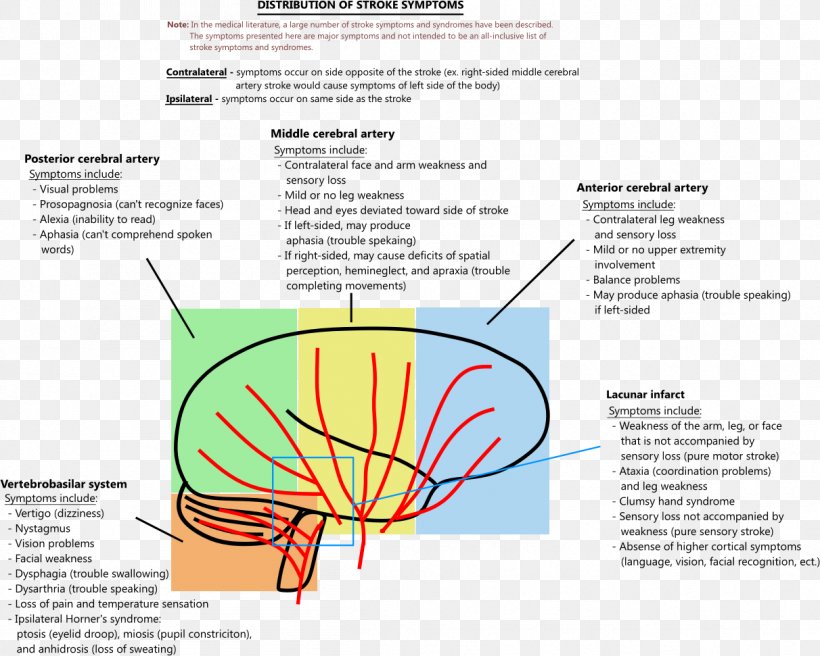
Posterior Cerebral Artery Syndrome
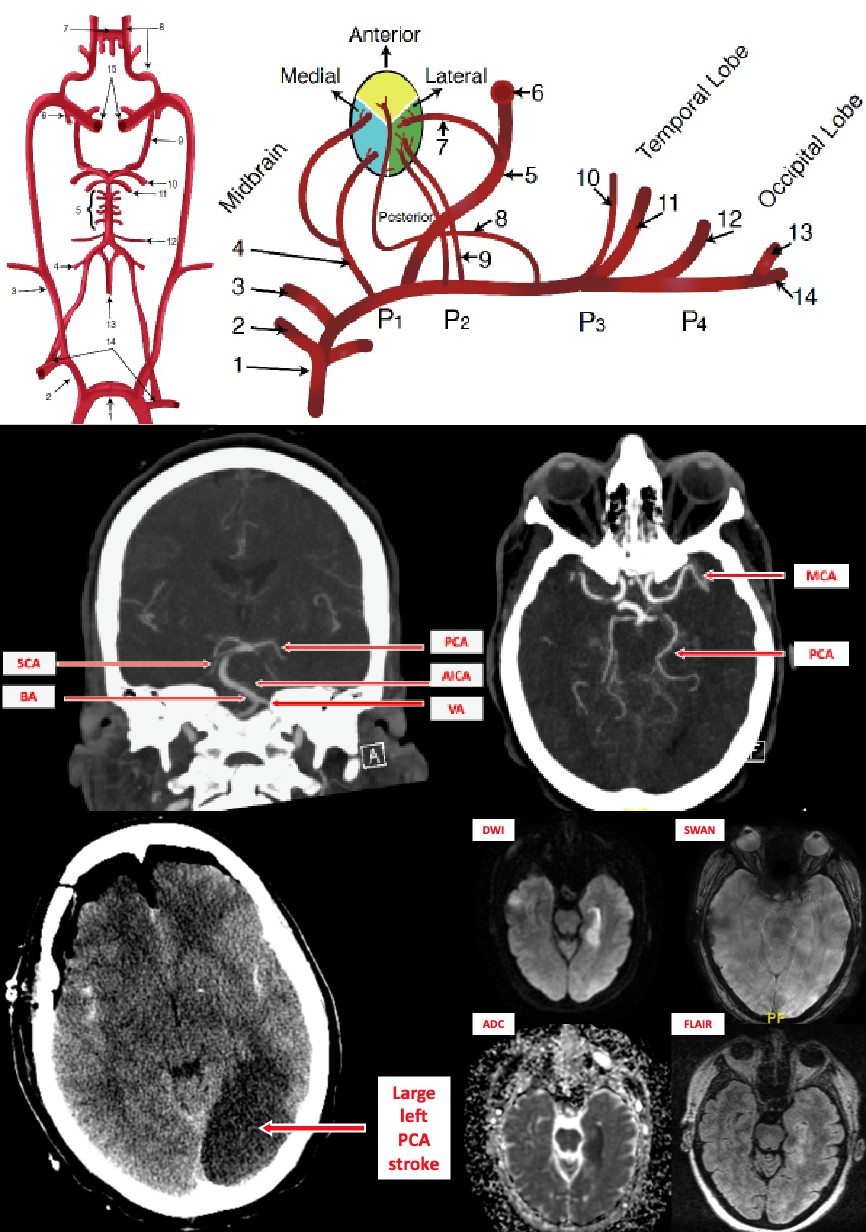
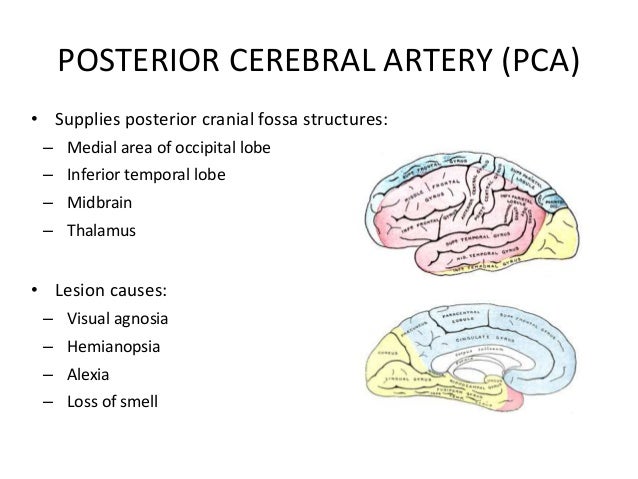
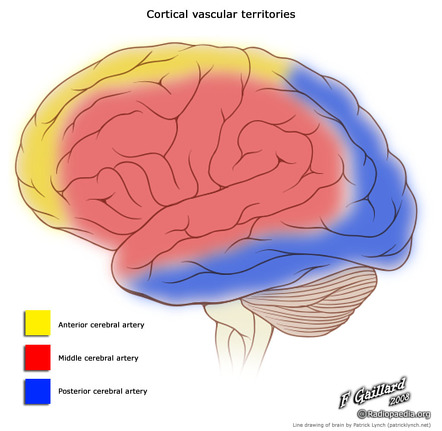
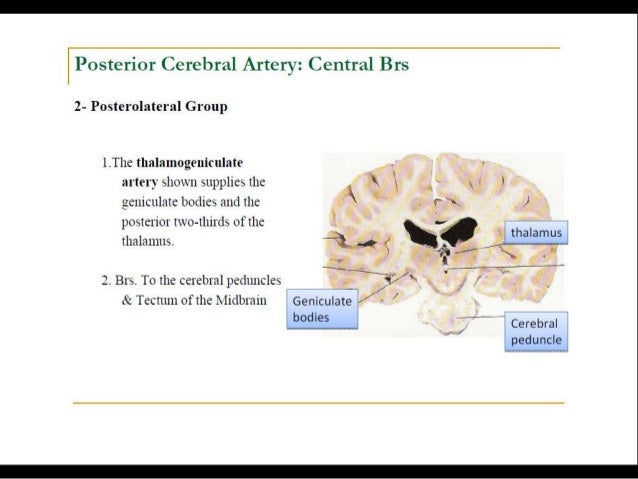
Posterior cerebral artery syndrome. A posterior infarction is usually caused by occlusion of which coronary artery. The occipital lobe the inferomedial temporal lobe a large portion of the thalamus and the upper brainstem and midbrain. A solid understanding of the pathophysiology of a posterior cerebral artery PCA stroke as well as the syndrome relating to it requires adequate knowledge of the structures and vascular anatomy of the brain.
Asked Dec 12 2016 in Health Professions by Logic. This is further complicated in that patients are not always aware of their symptoms making it more difficult to establish a timeline. Posterior cerebral artery syndrome is a condition whereby the blood supply from the posterior cerebral artery PCA is restricted leading to a reduction of the function of the portions of the brain supplied by that vessel.
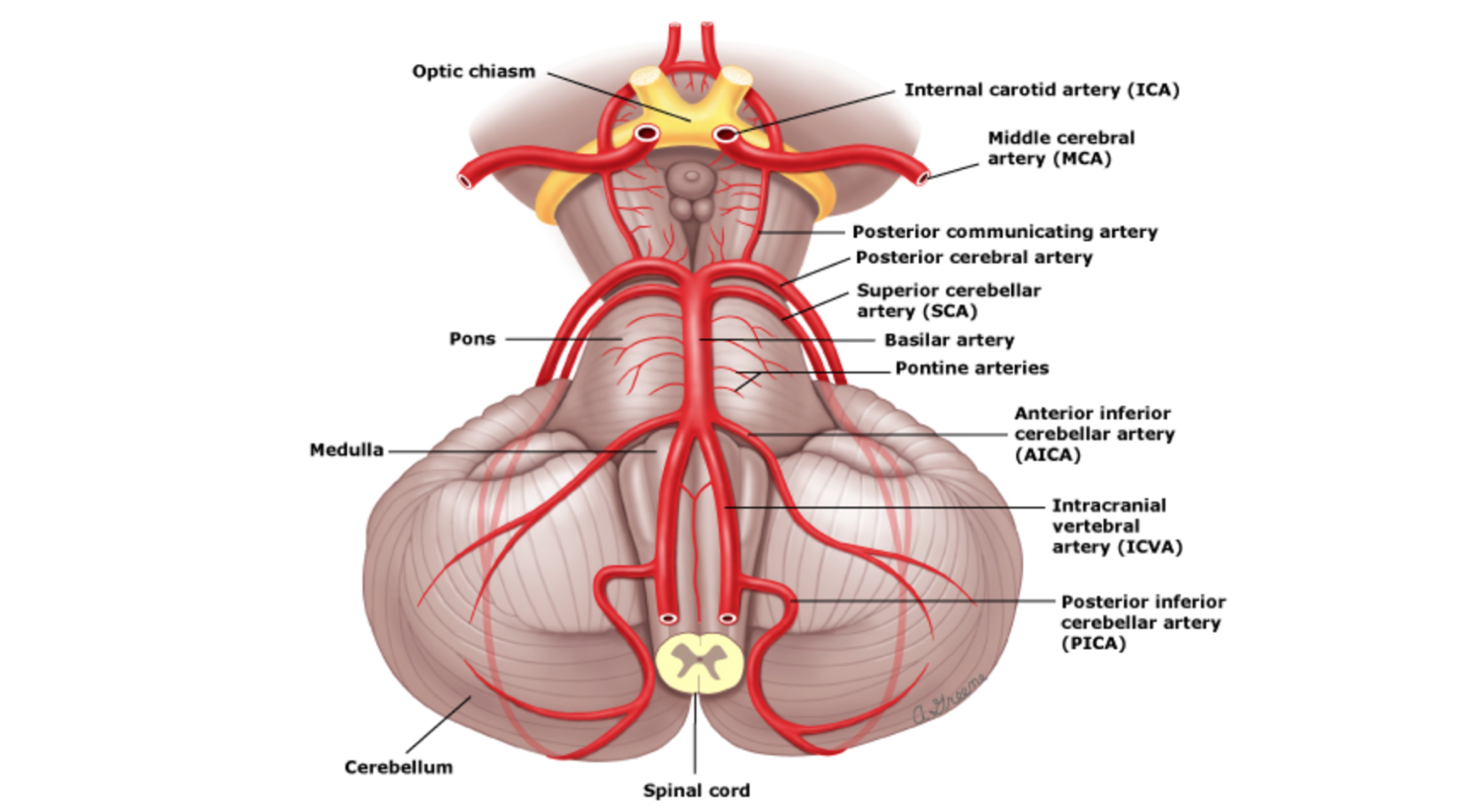
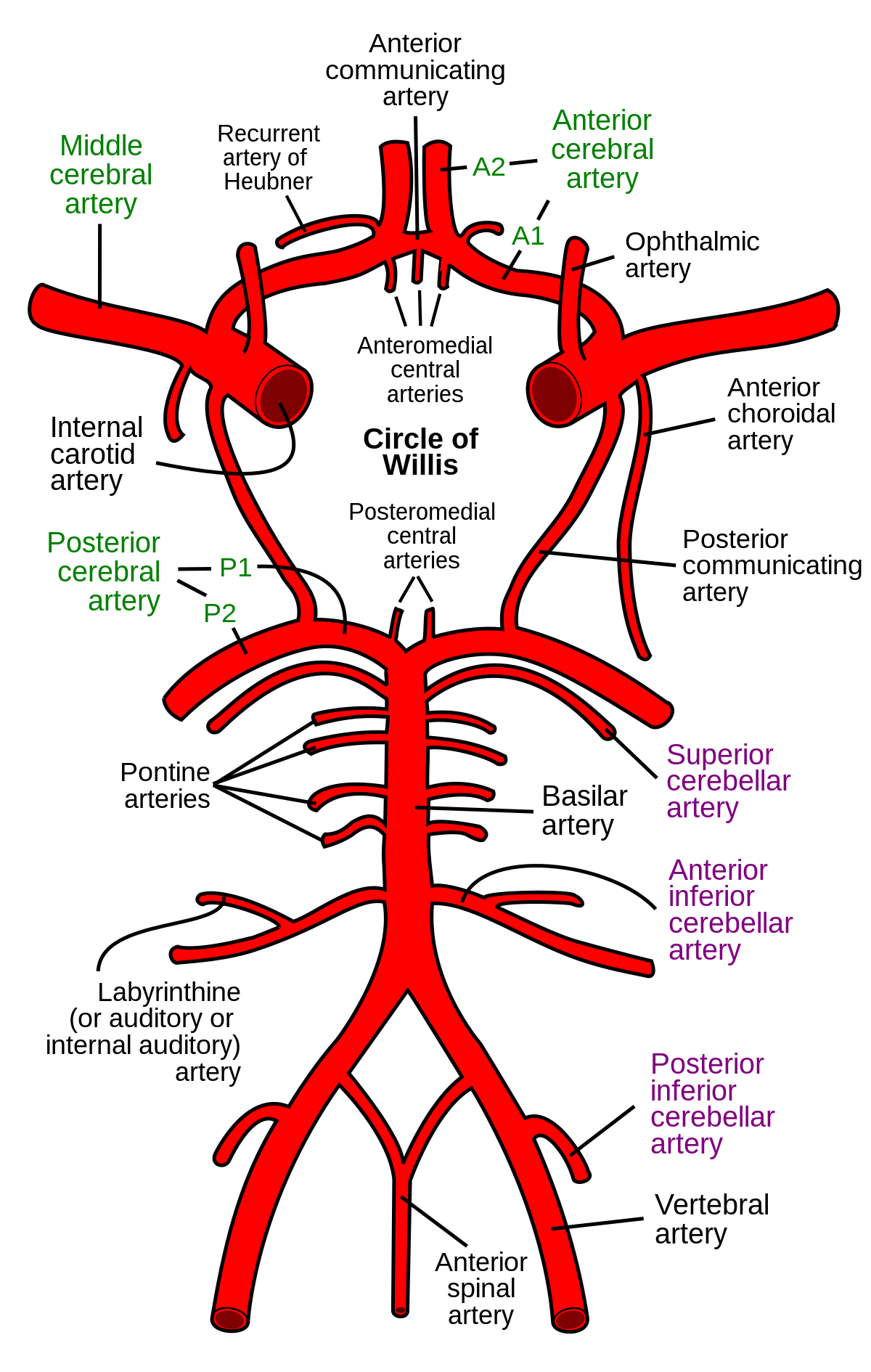
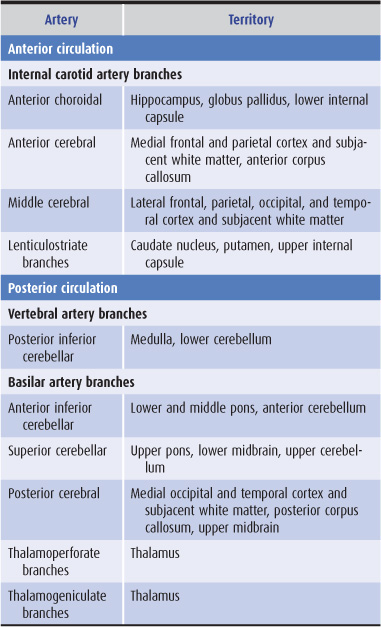
Posterior Cerebral Artery Superior Cerebellar Artery Middle Basilar Artery Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery Lower Vertebral Artery. Occlusion of the internal carotid artery can cause. The posterior cerebral artery PCA is one of a pair of arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe part of the back of the human brain.
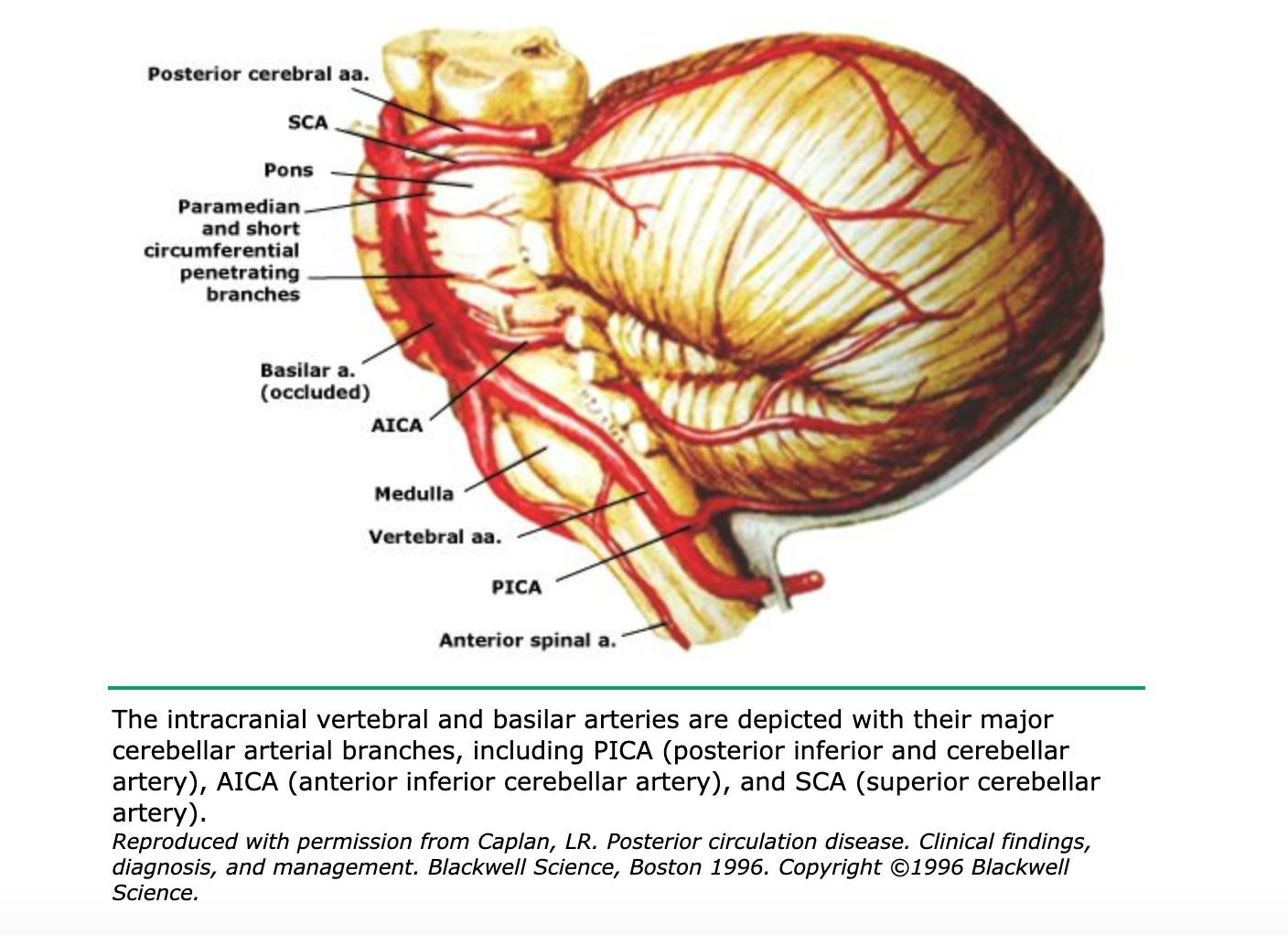
Knight W 2015. Lateral medullary syndrome is also called Wallenbergs syndrome posterior inferior cerebellar artery. Focus on Stroke.
Posterior cerebral artery syndrome is characterized by. Lateral medullary syndrome Wallenbergs syndrome - A case report. There may be some disturbance of higher function such as altered memory or speech or cortical blindness.
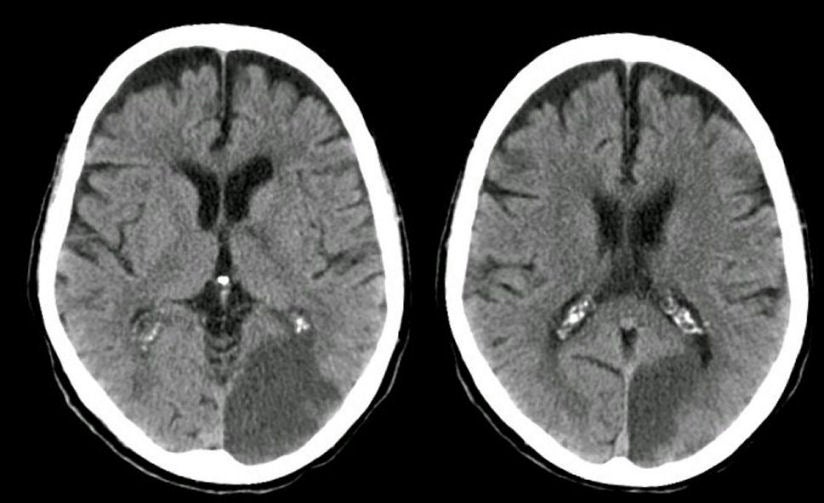
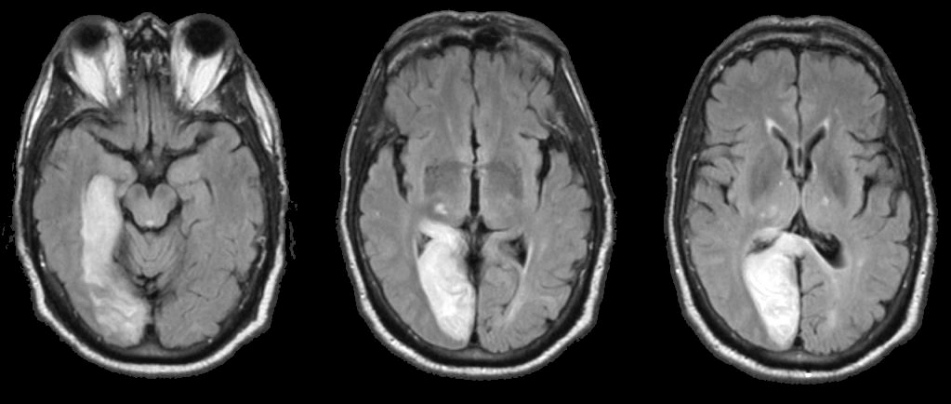
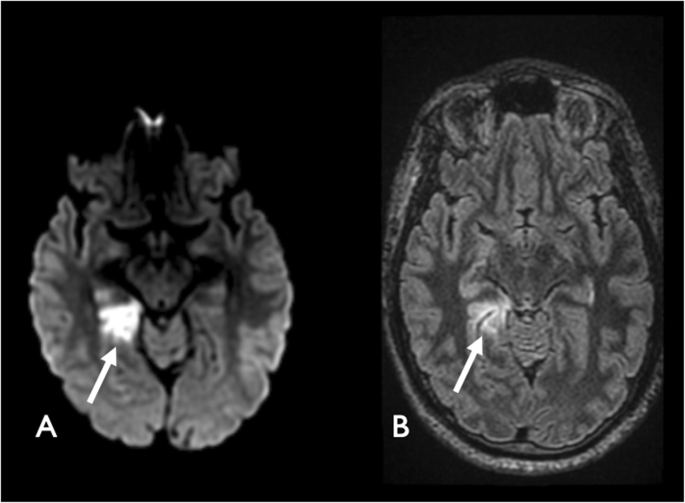
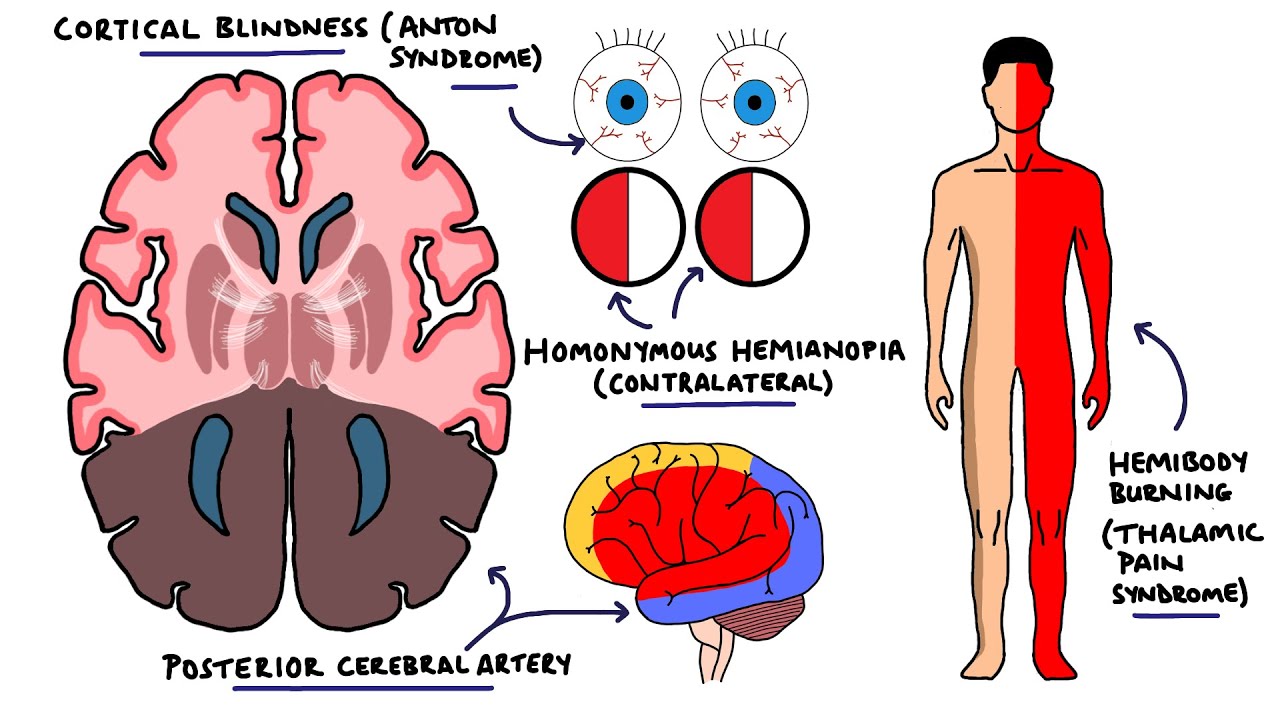
Faridpur Medical College Journal 51 35-36. Clinical presentation Symptoms of posterior cerebral artery stroke include contralateral homonymous hemianopia due to occipital infarction hemisensory loss due to thalamic infarction and hemi-body pain usually burning in nature and due to thalamic infarction 3. Posterior cerebral artery PCA strokes can be challenging to diagnose due to the variability in symptoms which may be nonspecific and inconsistent upon initial presentation.
Anterior and posterior circulations provide the primary blood circulation of the brain. Posterior cerebral artery stroke by reverse flow embolism in thoracic outlet syndrome - a case report Very few cases of stroke in arterial thoracic outlet syndrome have been described with thorough dynamic vascular imaging.
Knight W 2015.
Lateral medullary syndrome Wallenbergs syndrome - A case report. This is further complicated in that patients are not always aware of their symptoms making it more difficult to establish a timeline. Clinical presentation Symptoms of posterior cerebral artery stroke include contralateral homonymous hemianopia due to occipital infarction hemisensory loss due to thalamic infarction and hemi-body pain usually burning in nature and due to thalamic infarction 3. Lateral medullary syndrome is a neurological disorder causing a range of symptoms due to ischemia in the lateral part of the medulla oblongata in the brainstemThe ischemia is a result of a blockage most commonly in the vertebral artery or the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. Focus on Stroke. The occipital lobe the inferomedial temporal lobe a large portion of the thalamus and the upper brainstem and midbrain. Anterior and posterior circulations provide the primary blood circulation of the brain. There may be some disturbance of higher function such as altered memory or speech or cortical blindness. If bilateral often there is reduced visual-motor coordination 3.
There may be some disturbance of higher function such as altered memory or speech or cortical blindness. There may be some disturbance of higher function such as altered memory or speech or cortical blindness. Knight W 2015. Posterior cerebral artery PCA strokes can be challenging to diagnose due to the variability in symptoms which may be nonspecific and inconsistent upon initial presentation. This is further complicated in that patients are not always aware of their symptoms making it more difficult to establish a timeline. Anterior and posterior circulations provide the primary blood circulation of the brain. Clinical presentation Symptoms of posterior cerebral artery stroke include contralateral homonymous hemianopia due to occipital infarction hemisensory loss due to thalamic infarction and hemi-body pain usually burning in nature and due to thalamic infarction 3.

























Post a Comment for "Posterior Cerebral Artery Syndrome"