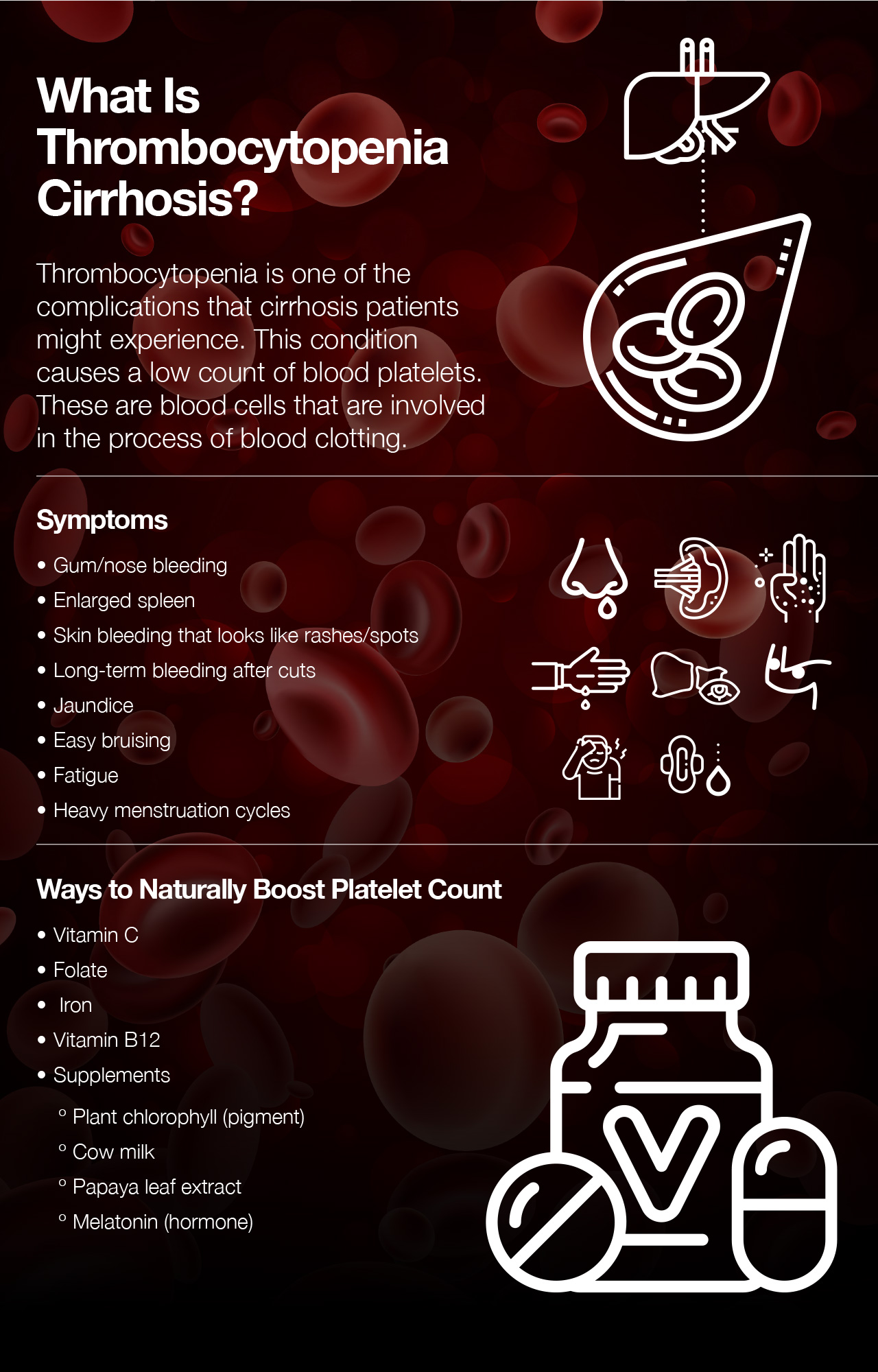
Thrombocytopenia And Liver Disease
Thrombocytopenia and liver disease. Thrombocytopenia is the most common hematologic complication associated with chronic liver disease CLD with important clinical implications. Thrombocytopenia is the most common hematological abnormality encountered in patients with chronic liver disease CLD. Thrombocytopenia defined as a platelet count.
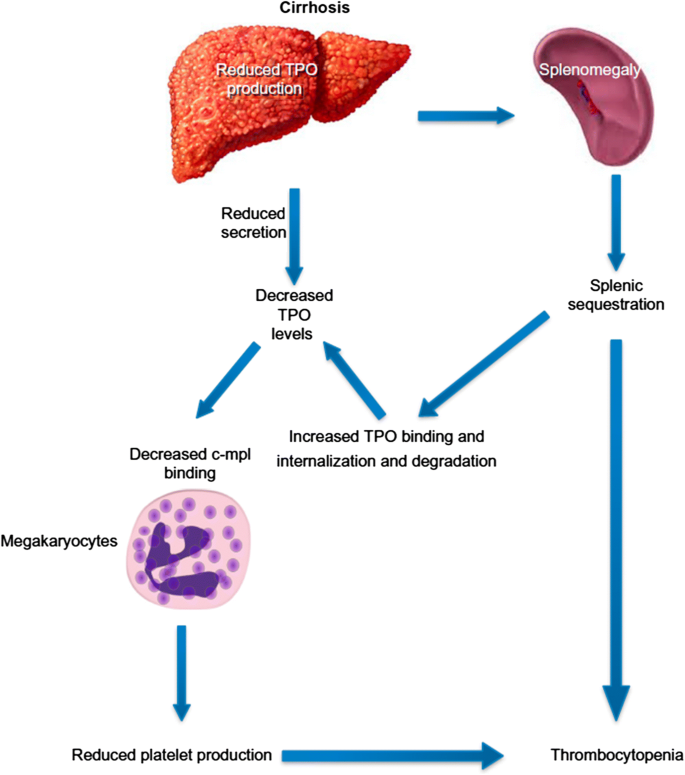
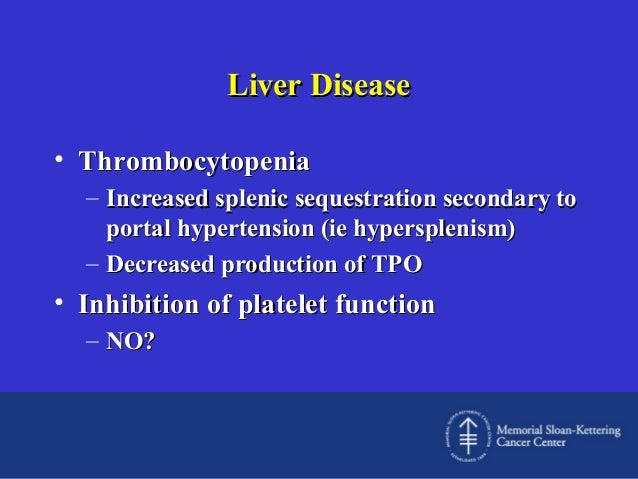
The pathophysiology of thrombocytopenia. Bleeding may complicate care of patients with both end-stage renal disease ESRD and cirrhosis. Thrombocytopenia in liver disease was exclusively due to increased pooling of platelets in an enlarged spleen secondary to portal hypertension and extensive cirrhosis 6.
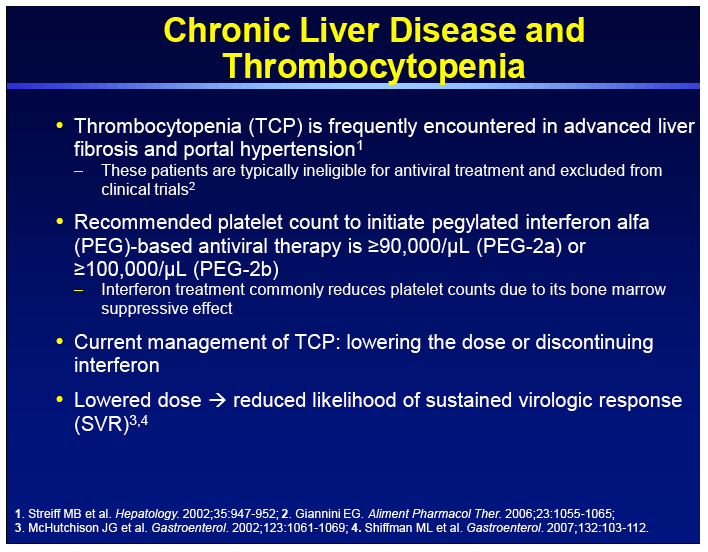
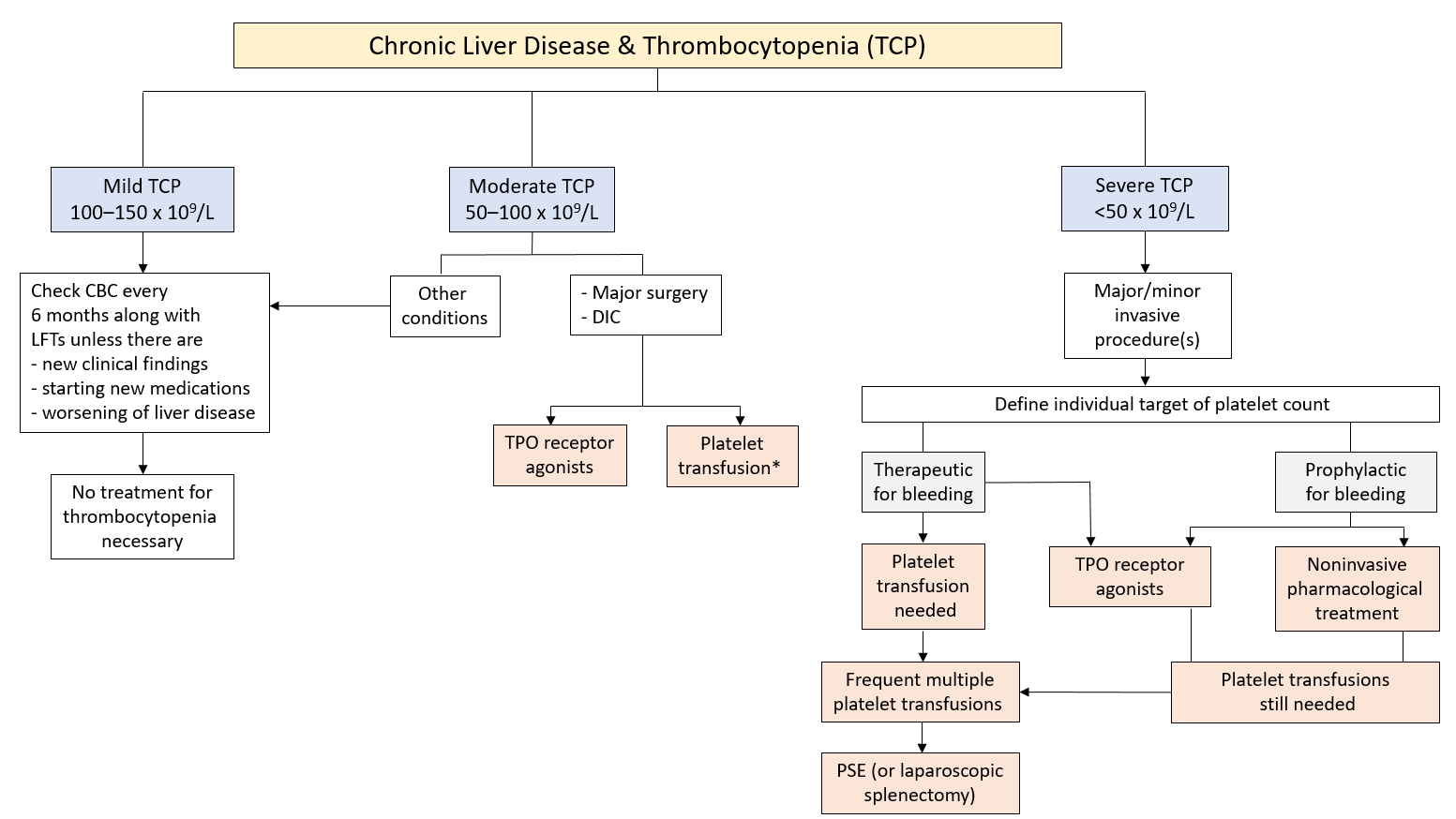
A decrease in platelet count can be the first presenting sign and tends to be proportionally related. Penia1 Thrombocytopenia can often be used as a marker of advanced liver disease and some studies have shown moderate-to-severe thrombocytopenia to be a strong in-dependent predictor of mortality23 Mild-to-moderate thrombocytopenia rarely has any clinical significance be-cause spontaneous bleeding is unlikely to occur at these levels. Thrombocytopenia is one of the most common hematological abnormalities and is often the first abnormality seen in patients with chronic liver disease.
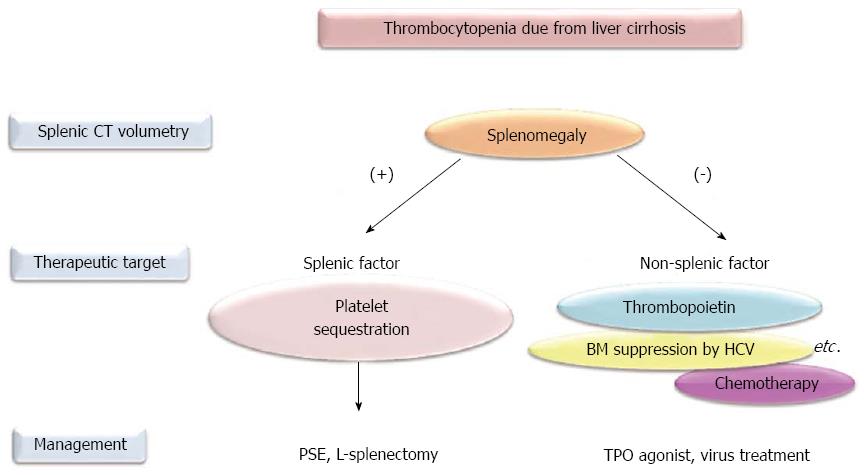
The pathophysiology of thrombocytopenia in liver disease has long been associated with the concept of hypersplenism where portal hypertension was thought to cause pooling and sequestratio. Liver disease was the most common cause for thrombocytopneia in outpatients a common phenomenon caused by portal hypertension and congestive splenomegaly. Platelet sequestration such as in someone with a large spleen or with liver disease.
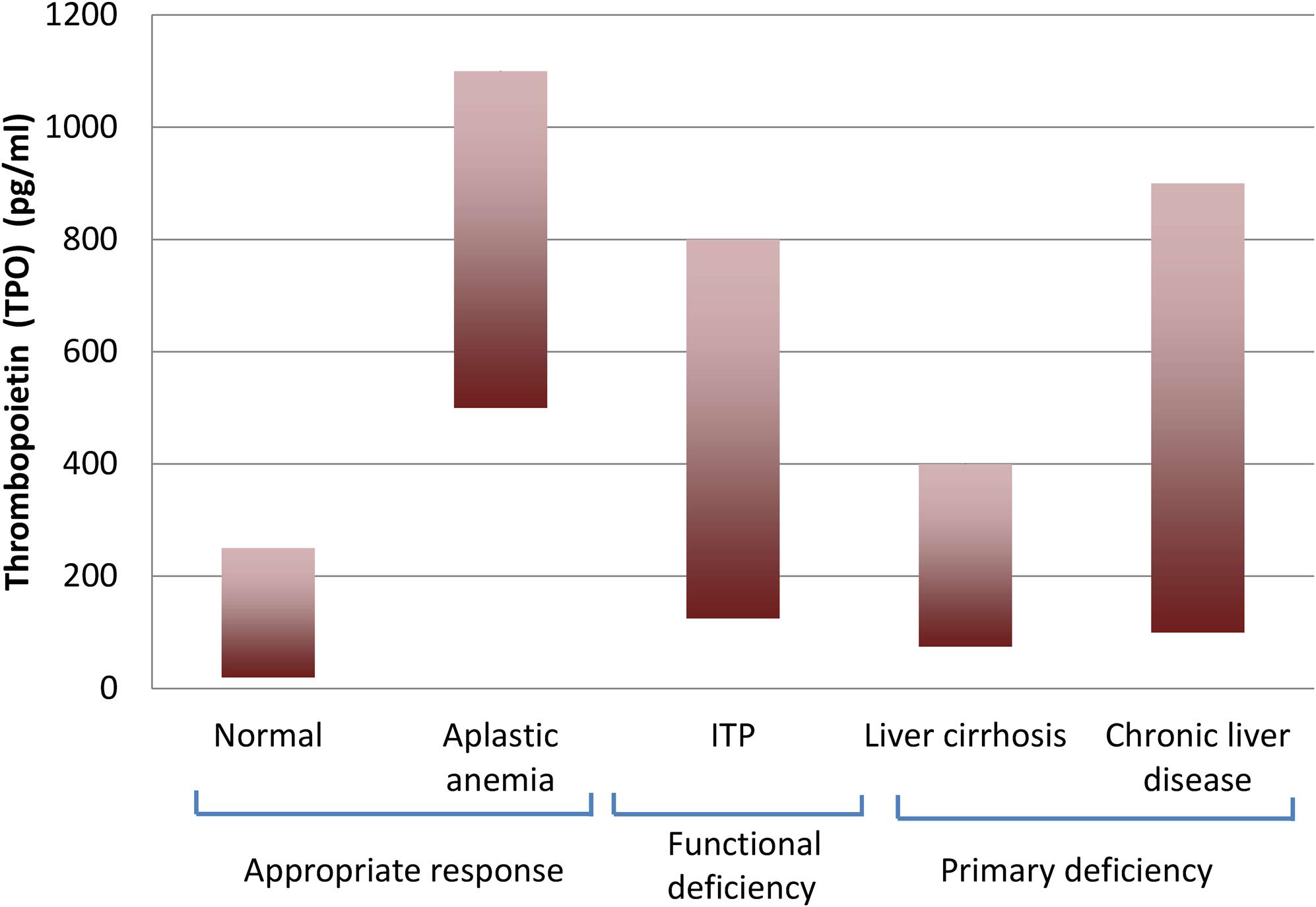
Thrombocytopenia in liver disease Moderate thrombocytopenia is a frequent finding in cirrhosis of the liver and well tolerated in most instances. While the mechanisms for thrombocytopenia are multifactorial platelet sequestration in the spleen and decreased thrombopoietin TPO production are the main mechanisms in patients with CLD. Historically thrombocytopenia has been attributed to hypers.
Thrombocytopenia is a common and challenging clinical disorder in patients with chronic liver disease. Thrombocytopenia affects approximately 6 of patients without cirrhosis and 70 of patients with cirrhosis. Thrombocytopenia is a common complication in liver disease and liver disease-related thrombocytopenia is often defined as a platelet count 100 10 9 L including moderate less than 100 10 9 L and severe less than 50 10 9 L thrombocytopenia.
Decreased platelet production as occurs in certain bone marrow diseases. In addition to being an indicator of advanced disease and poor prognosis it frequently prevents crucial interventions.
A decrease in platelet count can be the first presenting sign and tends to be proportionally related to the severity of hepatic failure.
Thrombocytopenia affects approximately 6 of patients without cirrhosis and 70 of patients with cirrhosis. Platelet sequestration such as in someone with a large spleen or with liver disease. Thrombocytopenia is a common haematological disorder in patients with chronic liver disease. It is multifactorial and severity of liver disease is the most influential factor. Thrombocytopenia is the most common hematologic complication associated with chronic liver disease CLD with important clinical implications. Bleeding may complicate care of patients with both end-stage renal disease ESRD and cirrhosis. A decrease in platelet count can be the first presenting sign and tends to be proportionally related. Liver disease was the most common cause for thrombocytopneia in outpatients a common phenomenon caused by portal hypertension and congestive splenomegaly. Thrombocytopenia in liver disease was exclusively due to increased pooling of platelets in an enlarged spleen secondary to portal hypertension and extensive cirrhosis 6.
As a result of the increased risk of bleeding thrombocytopenia may impact upon medical procedures such as surgery or liver. Thrombocytopenia affects approximately 6 of patients without cirrhosis and 70 of patients with cirrhosis. Thrombocytopenia is the most common hematologic complication associated with chronic liver disease CLD with important clinical implications. It is multifactorial and severity of liver disease is the most influential factor. A decrease in platelet count can be the first presenting sign and tends to be proportionally related to the severity of hepatic failure. The three main classes of thrombocytopenia are. It is multifactorial and severity of liver disease is the most influential factor.





































Post a Comment for "Thrombocytopenia And Liver Disease"